However, inspite of all the goodies attached, you might occasionally come across a few bugs and issues as well. Among them, it’s the inability of the wireless network to function along the expected lines that could prove to be one of the most infuriating and concerning issues for the end-user. If you ever come across this WiFi not working issue on your Android 13 device, then the below-listed methods shall help you rectify it once and for all. Follow along for the fixes.
How to Fix WiFi not working in Android 13
Do note that the methods listed below are applicable across all the devices that are running the latest Android 13. While the setting names might be slightly different (such as WiFi and Internet instead of WiFi and Network), but the underlying steps will be near-about identical. Moreover, there’s no universal fix as such, You will have to try out each of the below-listed workarounds and then see which one spells out success for you. So with that in mind, let’s get started.
FIX 1: Restart Device
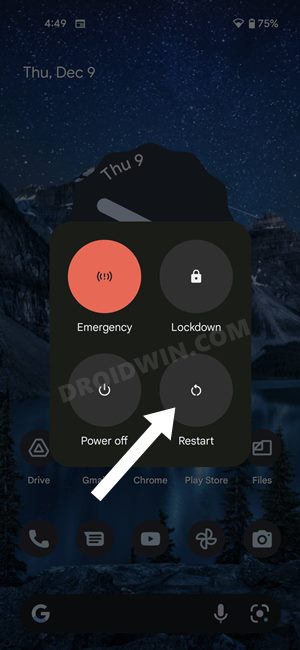
First and foremost, you should try out the basic troubleshooting tips, which involve restarting your device. While it may sound like an obvious fix, but trust us, in most instances, a simple reboot is enough to rectify most of the issues.
FIX 2: Toggle WiFi
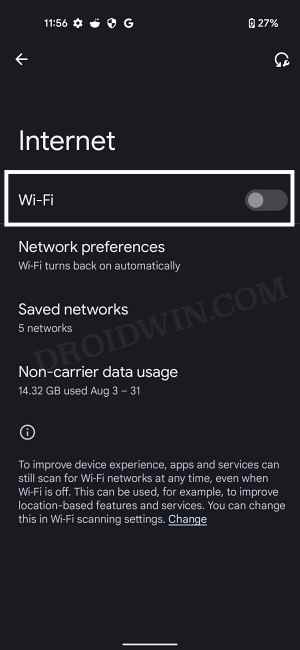
Your next course of action should be to toggle off/on the WiFi on your device. This will refresh the WiFi settings and could rectify the underlying issue. So let’s put it to the test and check out the results.
FIX 3: Toggle Airplane Mode
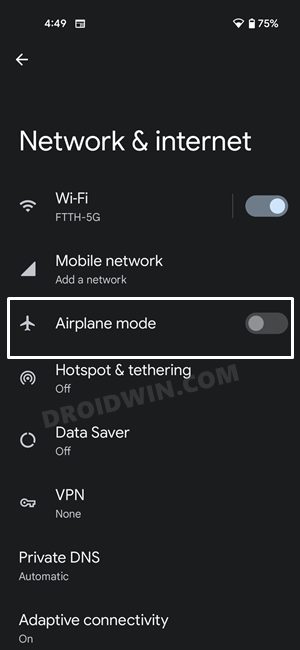
Toggling on/off the Airplane Mode will disable and then re-enable all the mobile networks. This will then give these networks a fresh instance to work upon and hence the issue might be resolved in this fresh environment. So let’s put this method to test right away:
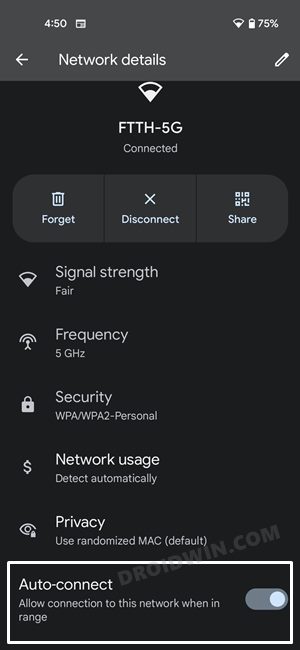
FIX 4: Enable Auto Connect
Enabling Auto Connect for your WiFi will instruct your device to automatically connect to that saved network if it is nearby to your location. So consider enabling this feature, which could be done as follows:
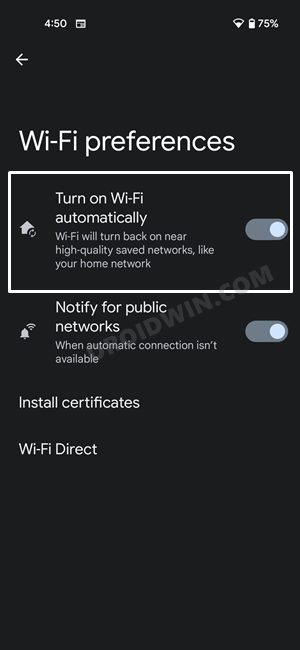
FIX 5: Enable Turn on WiFi Automatically
This feature will turn on the WiFI automatically as soon as it is nearby a saved network. After that, it will scan for the networks whose passwords are saved inside the data directory of your device and would then automatically connect it to the one that has the strongest signal. So you should consider enabling this feature, using the instructions given below.
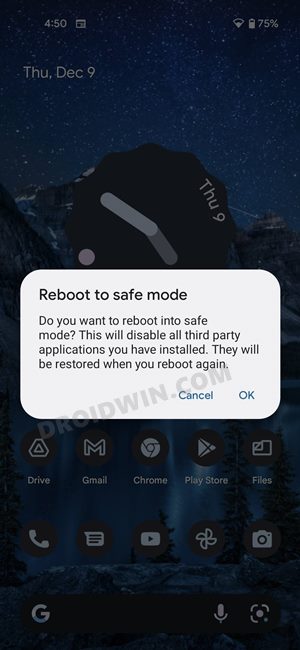
FIX 6: Boot to Safe Mode
In some instances, a third-party app might conflict with the mobile network. To verify if that is the case and then rectify this issue, you will have to boot your device to the Safe Mode. This will disable all the third-party apps and your device will only be running with the stock apps that were initially present on your device. If you are able to use WiFi in this mode, then the culprit is indeed a third-party app. Therefore you should consider uninstalling all those apps, one at a time, after which the WiFi issues first started happening, The last app you remove which ends up fixing the issue would be the reason behind this problem. So it’s better to maintain a safe distance from that app in the near future as well and look for its alternatives. Moreover, you may now re-install all the other uninstalled apps.
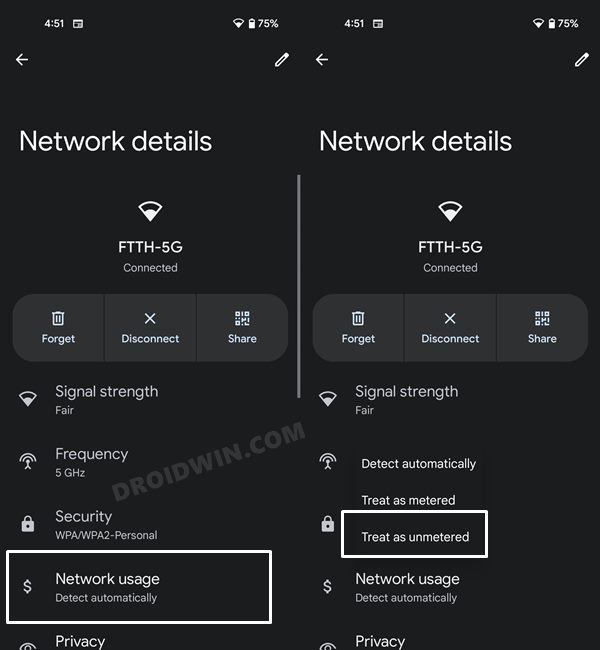
FIX 7: Disable Metered WiFi Connection
Metered WiFi connection puts a cap on the maximum bandwidth that could be consumed during a particular period of time. Once you reach that limit, it will then prevent your device from accessing the internet any further.
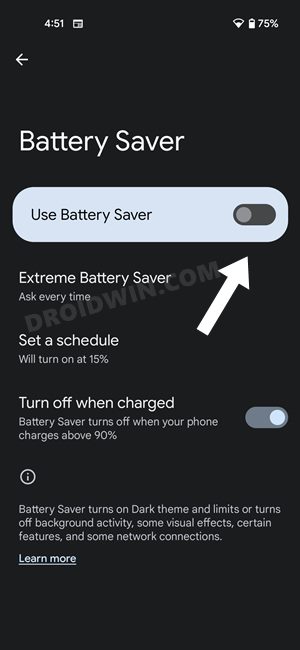
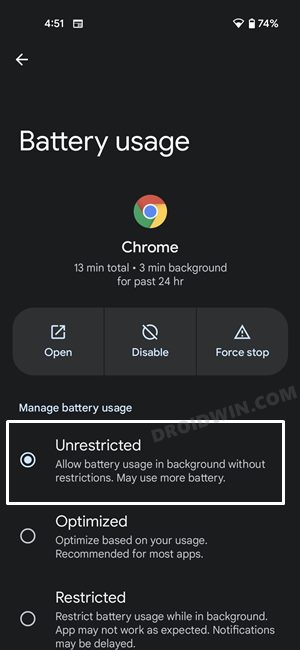
FIX 8: Disable Battery Saver/Optimizations
If you have enabled the battery saver mode or put any restrictive measures in place, then consider disabling them for now. This is because, in order to preserve the battery, these features tend to stop all the background activities, and that includes disabling apps from accessing the internet in the background, Along the same lines, it will also stop the app’s background sync functionality over to the servers. So disabling them would prove to be the best approach and you could try it out using the below listed steps:
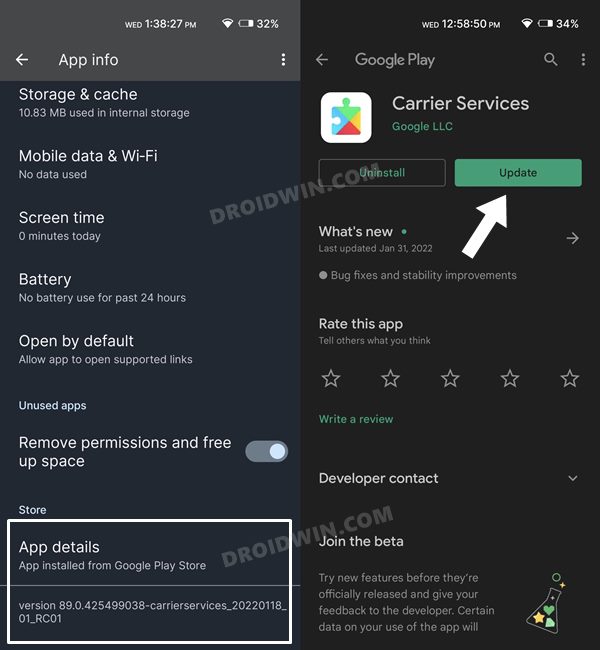
FIX 9: Update Carrier Service
In most cases, the Carrier Service is automatically updated to the latest version alongside the latest monthly updates. However, sometimes that might not be the case [February 2022 update for Pixel 6/Pro] and you would have to manually carry out this update. So refer to the below instruction steps to check out the Carrier version on your device and then subsequently update it to the latest one:
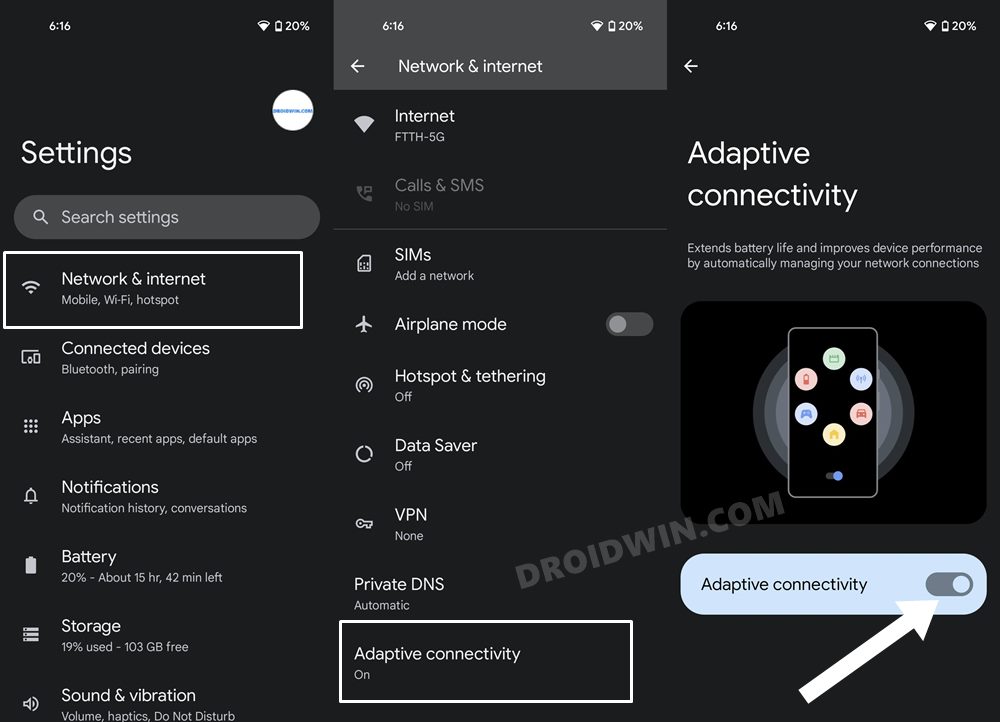
FIX 10: Disable Adaptive Connectivity
The Adaptive Connectivity feature checks for your current network requirement, and if it finds it isn’t on the higher side, it switches from 5G to 4G, thereby resulting in battery saving. However, this functionality seems to be playing a part in all the network and call-related issues that we have documented to date, and there might be a chance that it could be the culprit this time around as well. So you could try disabling this feature for the time being and then check out the results.
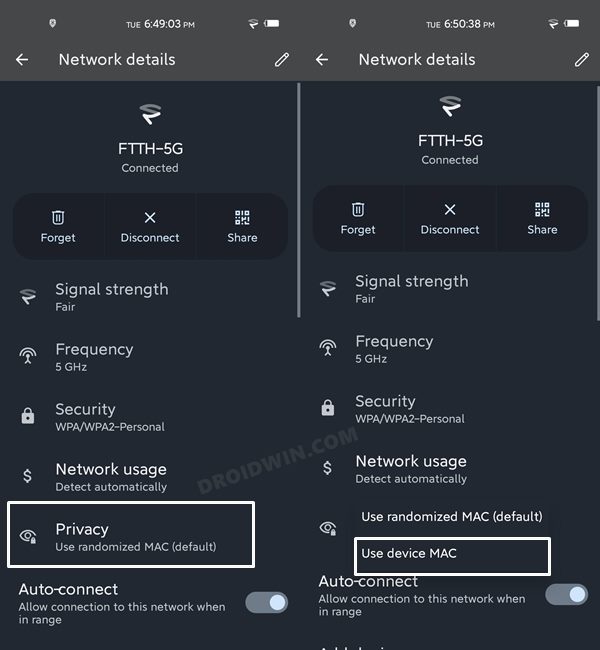
FIX 11: Switch to Default Mac Address
The MAC (Media Access Control) Address is a unique identifier that has been assigned to your device network card. By default, your device is assigned a randomized MAC, however, for some users, this randomized MAC isn’t appearing on their device. So your next course of action should be to switch to the Default Mac. Here’s how:
FIX 12: Disable Mobile Data Always Active
This is a developer setting enabled on your device which makes sure that the carrier data remains active even if you have your WiFi turned on. This is done for a faster network switch, such as in case the WiFi is down, your device would be able to directly switch over to the mobile data without any delay. While this feature is no doubt quite a handy one, but in some instances, it tends to conflict with the normal functionality of the wireless network. So you should consider disabling it, via the below steps:
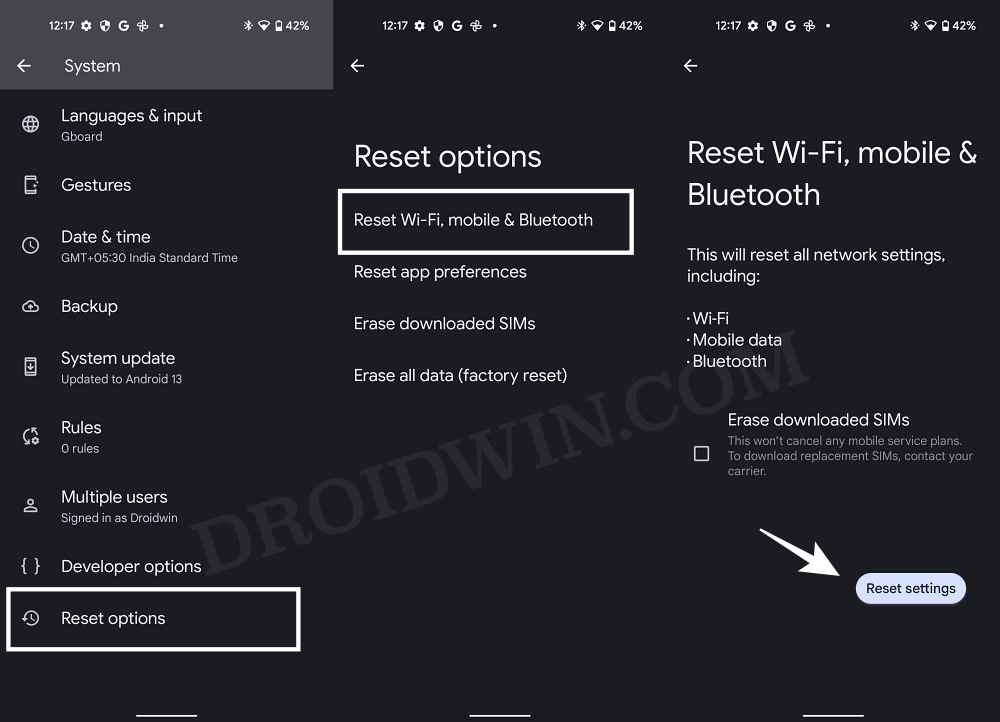
FIX 13: Reset Network Settings
If the stored network data gets corrupted, then it could spell out trouble for the entire network configuration on your device. Therefore the only way out is to reset the setting back to their factory default state. Do keep in mind that doing so will erase all the saved WiFi networks, so make sure that they are synced with your Google account. if that’s well and good, then let’s get started.
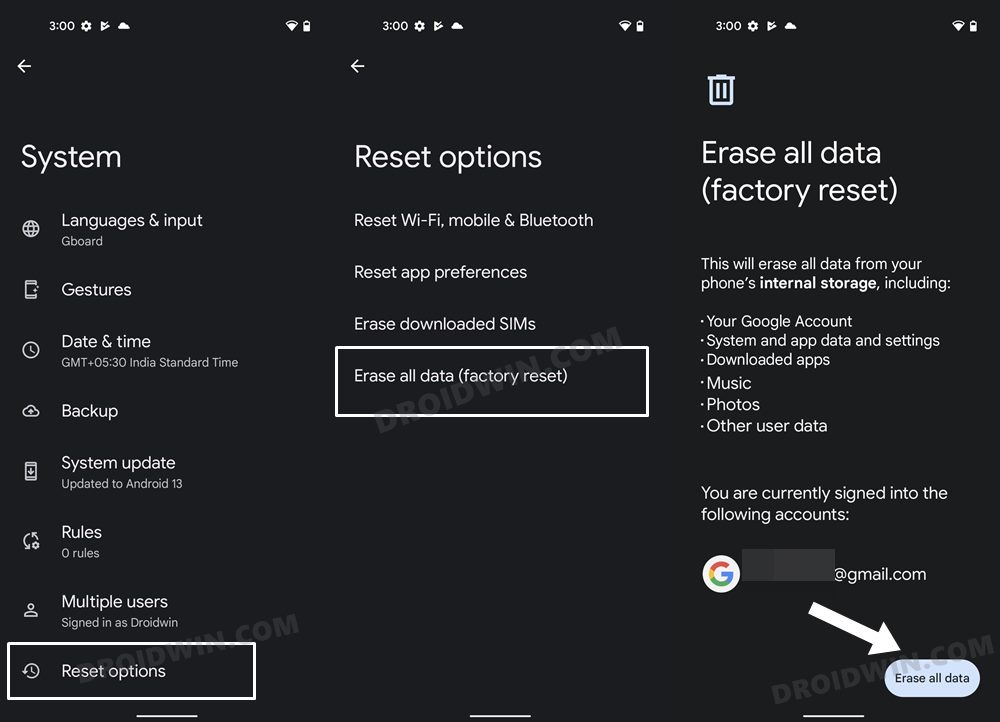
FIX 14: Reset Device
If none of the aforementioned methods managed to rectify the issue, then your last course of action should be to factory reset your device. This will delete all the data and bring the settings back to their default state- exactly how it was when you first unboxed your device. So it goes without saying that you should first take a backup of all the data (via Settings > System > Backup) and only then proceed with the below steps:
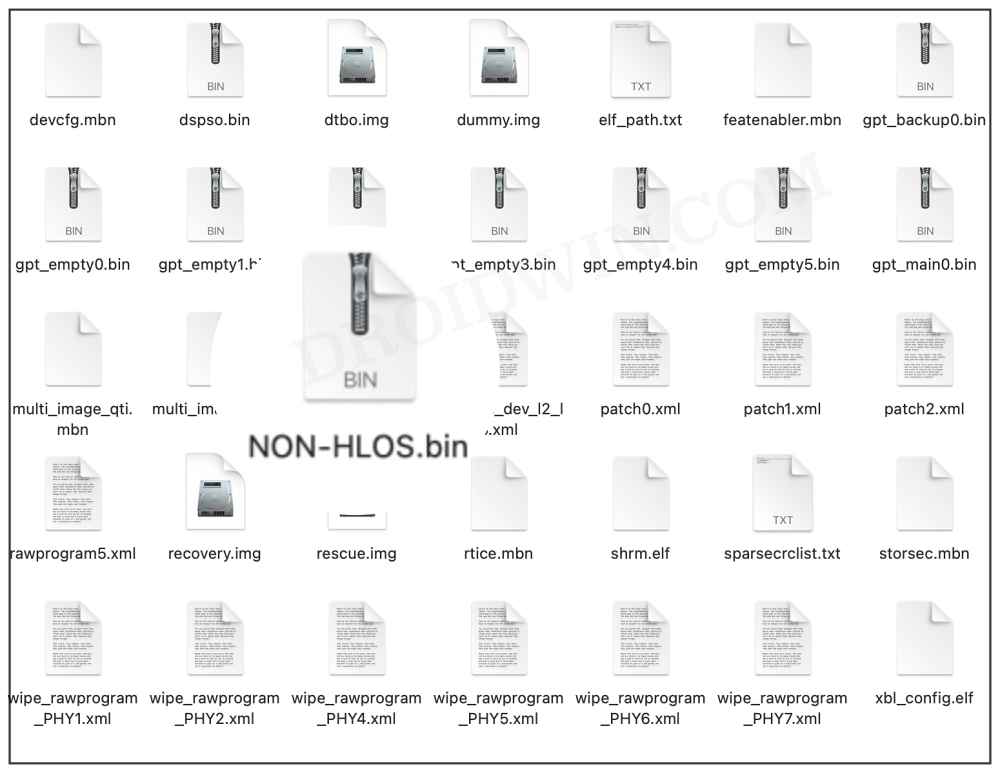
FIX 15: For Unlocked Bootloader Devices
If you are among those tech enthusiasts who like taking a stroll down the custom development, then there’s a possibility that you might have corrupted the modem partition. In that case, you will have to extract the modem file (NON-HLOS.bin or modem.bin) from the st0ck firmware and then flash it via Fastboot Commands. To try it out, please refer to any one of our below-listed guides which is in sync with your current needs.
How to Fix No WiFi, Calls, Network after Root, or Custom ROM.Fix Corrupt EFS/No IMEI/Network Issues [3 Methods].How to Flash Stock Firmware via Fastboot Commands.
That’s it. These were the various methods to fix the issue of WiFi not working on your Android 13 device. We have listed fifteen different methods for the same, do let us know which one worked out in your favor. Likewise, all your queries are welcomed in the comments section below.
Bring Back the WiFi toggle in Quick Settings on Android 13Device restarting when connecting to WiFi in Android 13Haptic Feedback not working in Gboard after Android 13 Update [Fix]Third-Party/Sideloaded Apps crashing in Android 13: How to Fix
About Chief Editor