As a result, that application might not be able to function along the expected lines and you would notice lags, stutters, and freezes inside that app, and in some instances, its effect could be felt across the system as a whole as well. This is where the Windows Hardware Acceleration feature comes in handy. For example, when you are running a high-end game, then the Hardware Acceleration would offload some work from the CPU and give it over to the GPU. Likewise, in the case of rendering software, the work might be shared between CPU, GPU, and the Video Card. The main motive in all these cases is to free up some load from the CPU so that it could function on essential system processes and provide you with a smooth and lag-free environment. So with this, you might have got a decent idea regarding how this feature works, let’s now turn our attention to the all-important question- how to enable Hardware Acceleration in Windows 11? Well, there exist three different methods for the same. Let’s check them out.
How to Enable Hardware Acceleration in Windows 11 [3 Methods]
There exist three different approaches to get this job done- the first one is via the Display Settings menu whereas the other two are via Registry Editor. We have listed the benefits and risks with all these three methods, so go through them once and then try out the one that is in sync with your requirement. [NOTE: it is highly recommended that you start with the first method].
Method 1: Via Display Settings
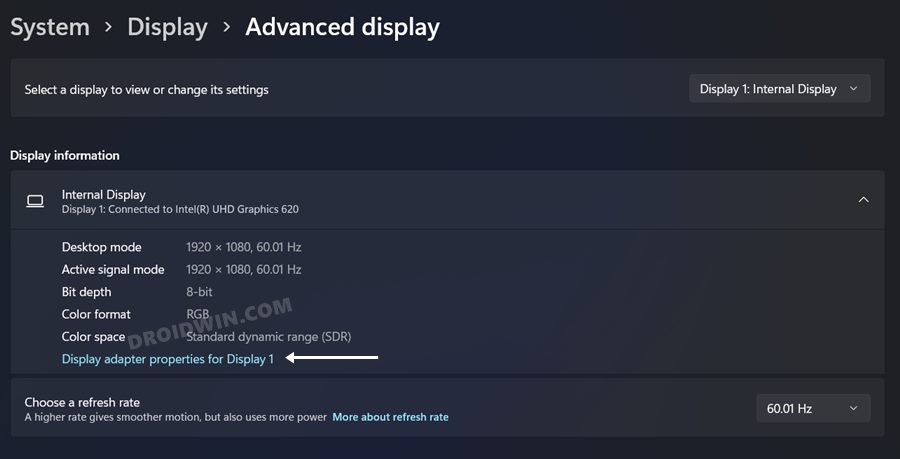
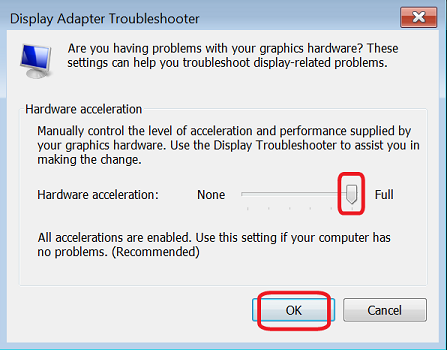
This is the most straightforward and easiest method and is also the recommended one as it will let you know beforehand whether your PC display supports Hardware Acceleration or not. And as you might have guessed, its downside is that as compared to Registry Editor, this method wouldn’t let you force-enable Hardware Acceleration on unsupported PCs (which infact might be a good thing). So on that note, let’s get started. NOTE: If the Troubleshoot tab is missing in the Graphics Properties dialog box (see below image) or if the Change Settings button under Troubleshoot is greyed out, then both these cases mean that your PC doesn’t support Hardware Acceleration. So your only option is to force enable it via Registry Editor, as explained in the below two methods.
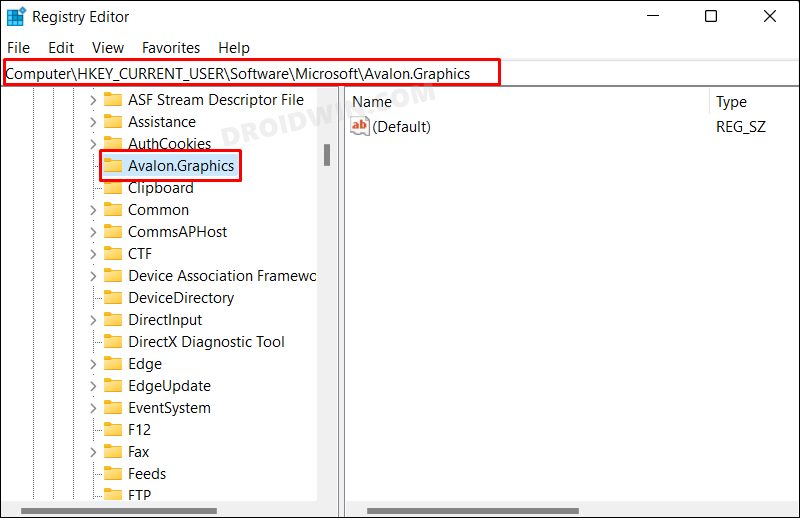
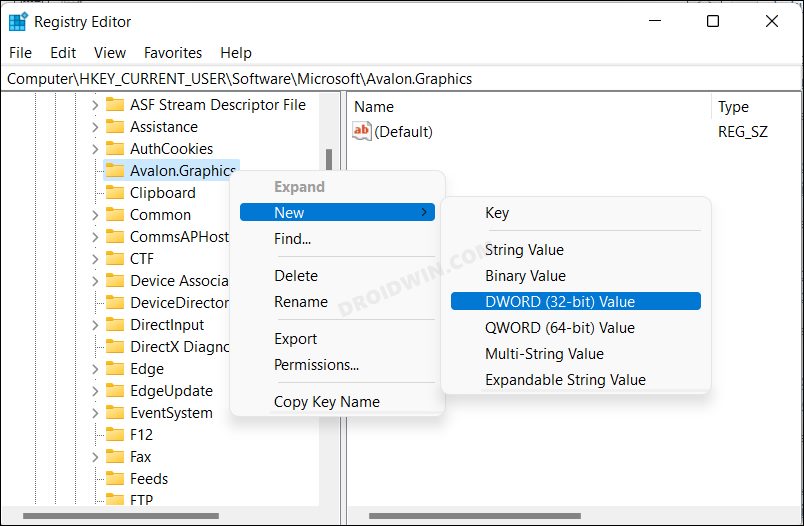
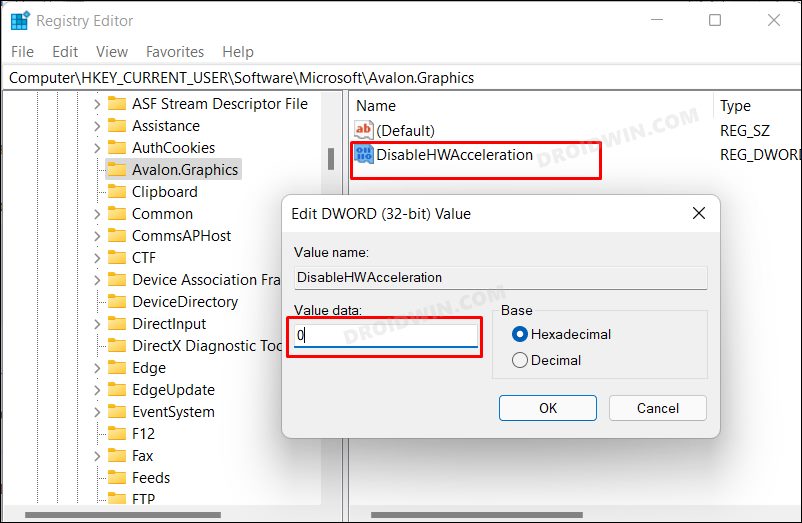
Method 2: Via Registry Editor
The advantage of this method is that it allows you to enable hardware Acceleration on PCs that don’t support it. And this could be its downside as well. Forcefully enabling this functionality on your unsupported PC could do more harm than good. Anyways, if you are willing to give it a try, then take a registry backup beforehand and then hop onto the below steps [try at your own risk].
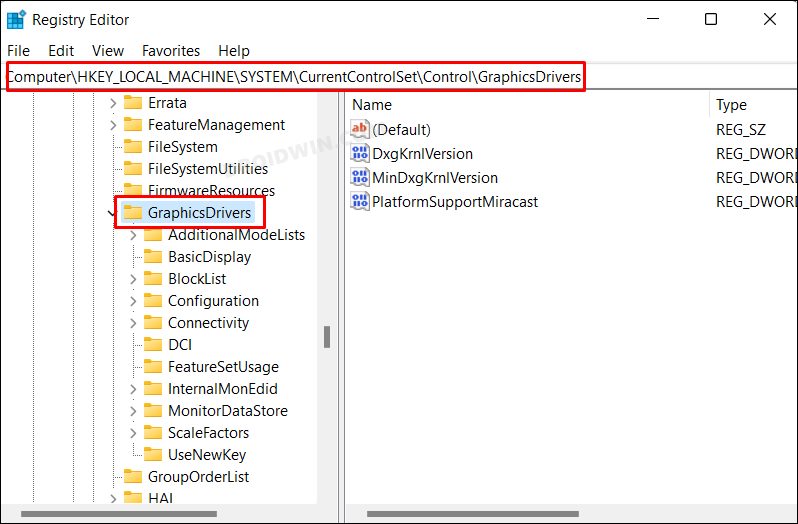
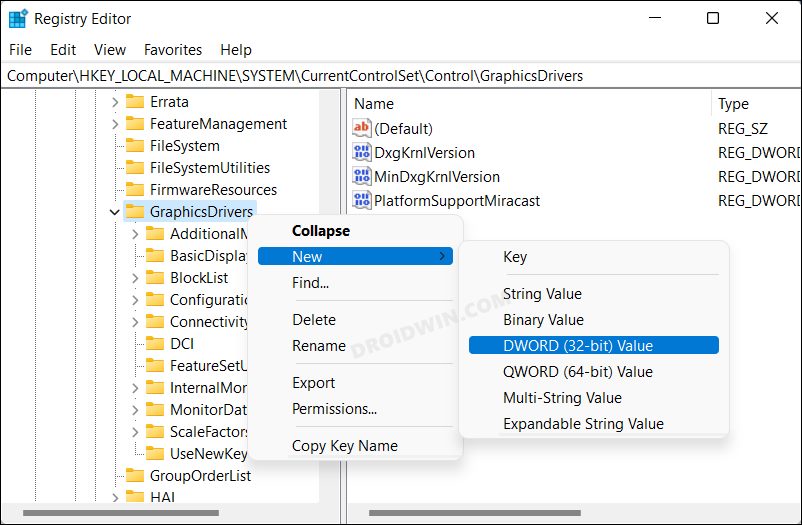
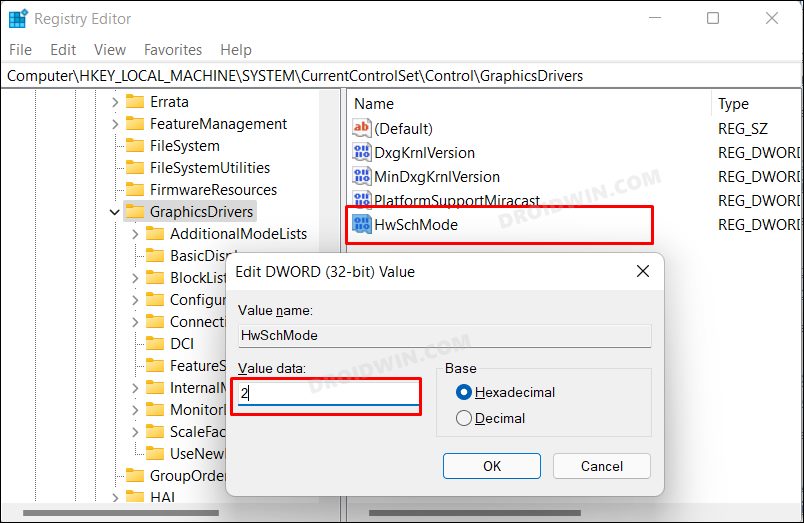
Method 3: Via Registry Editor
If the first Registry Editor method didn’t spell out success for you, then you could give this one a shot. It shares the same drawback and perks as the earlier one and you should take a registry backup before trying out the below steps [at your own risk]. With this, we round off the guide on how you could enable Hardware Acceleration in Windows 11. We have listed three different methods for the same. Do let us know in the comments which one you ultimately decided to try out. Likewise, all your queries are welcomed in the comments section below.
Enable and Use Hardware and Devices Troubleshooter in Windows 11How to Enable Local Security Policy secpol.msc in Windows 11 HomeEnable High and Ultimate Performance Power Plan in Windows 11How to Improve Gaming Performance in Windows 11 [15+ Methods]
About Chief Editor